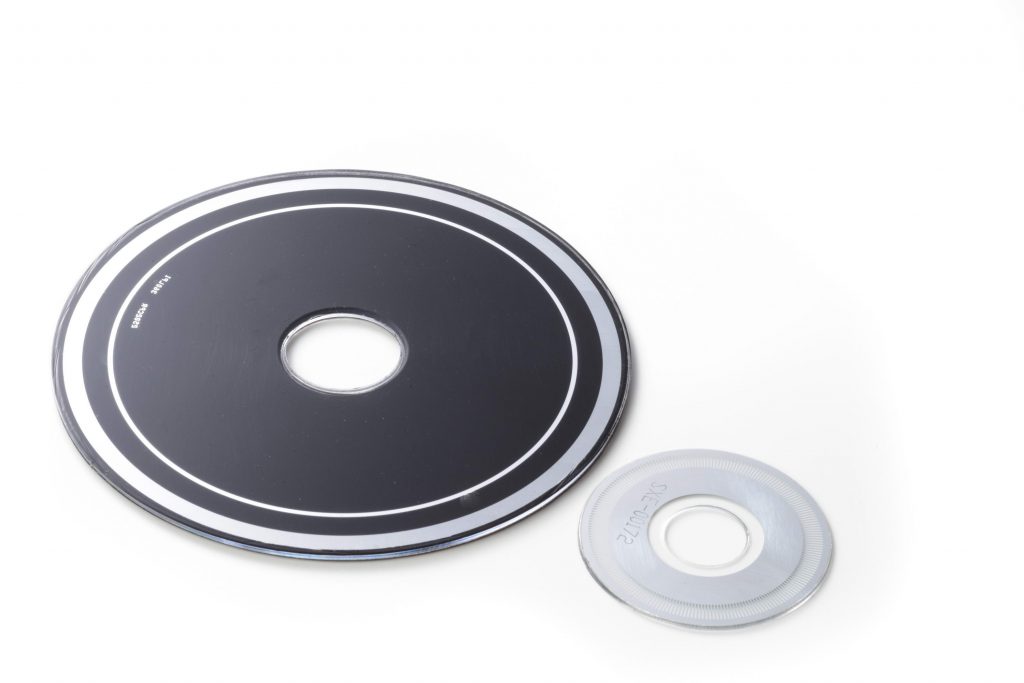
What is an optical encoder?
This type of encoder uses an optical sensor to detect whether light is on or off. This encoder characterized by its ability to handle high precision and high magnetic fields.
Optical encoders include reflective, transmissive, and diffraction grating types. Since ultra-thin stainless-steel plates or glass disks are used as rotating discs, mechanical vibration and shock may be a problem.

Fig. Optical Encoder
Optical encoders are widely used in office equipment, machine tools and industrial robots as high-precision position control sensors. In recent years, reflective encoders have been used in ultra-compact actuators and in cooperative robots that require a small amount of space.
Difference from Magnetic Encoders
There is a type of encoder called a “Magnetic Encoder” that is a counterpart to an optical encoder.
A magnetic encoder is a type of encoder that uses a magnetic sensor to detect changes in the magnetic field. They are simple, compact, and highly durable.
The magnetic type combines a magnetic drum and a magneto-electric conversion element such as a magneto-resistive element, and has a structure that can easily increase mechanical strength.
On the other hand, its disadvantage is that its resolution and accuracy are lower than those of optical encoders.This is because the resolution of magnetic encoders depends on the performance of the signal processing circuit, since the resolution is determined by the processing capacity of the electrical signal.
| Feature\Type | Optical Encoders | Magnetic Encoders |
|---|---|---|
| High resolution | ✓ | |
| High precision | ✓ | |
| Environmental resistance | ✓ | |
| Small size and light weight | ✓ | |
| Low price | ✓ |
Here are our products
Optical Encoder Wheels
Types of Optical Encoders
Optical encoders are classified by (1) Direction of motion to be measured, (2) Signal output method, and (3) Optical path.
1) Direction of motion to be measured
Optical Linear Encoders
This type of encoder irradiates light onto a slit pattern that moves along a linear axis, detects the light that passes through (or is reflected by) the pattern with a sensor, and outputs it as position information.
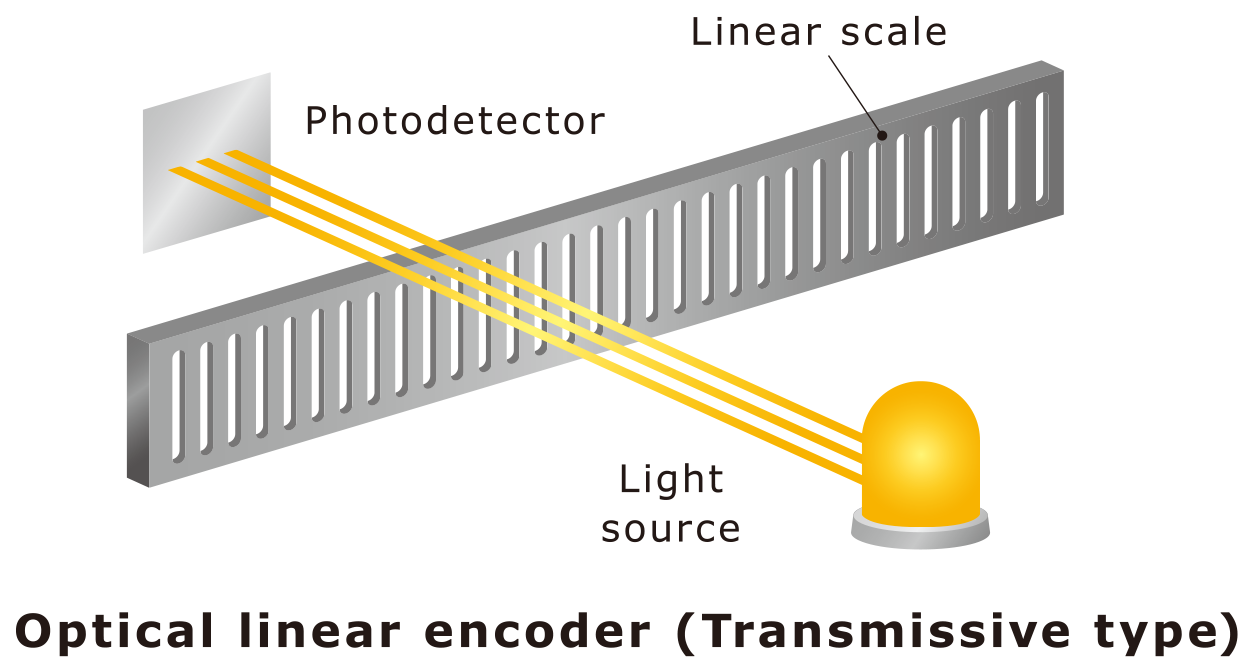
Optical Rotary Encoders
This type of encoder irradiates light onto a rotating slit pattern, detects the light that passes (or is reflected) by a sensor, and outputs it as position information.
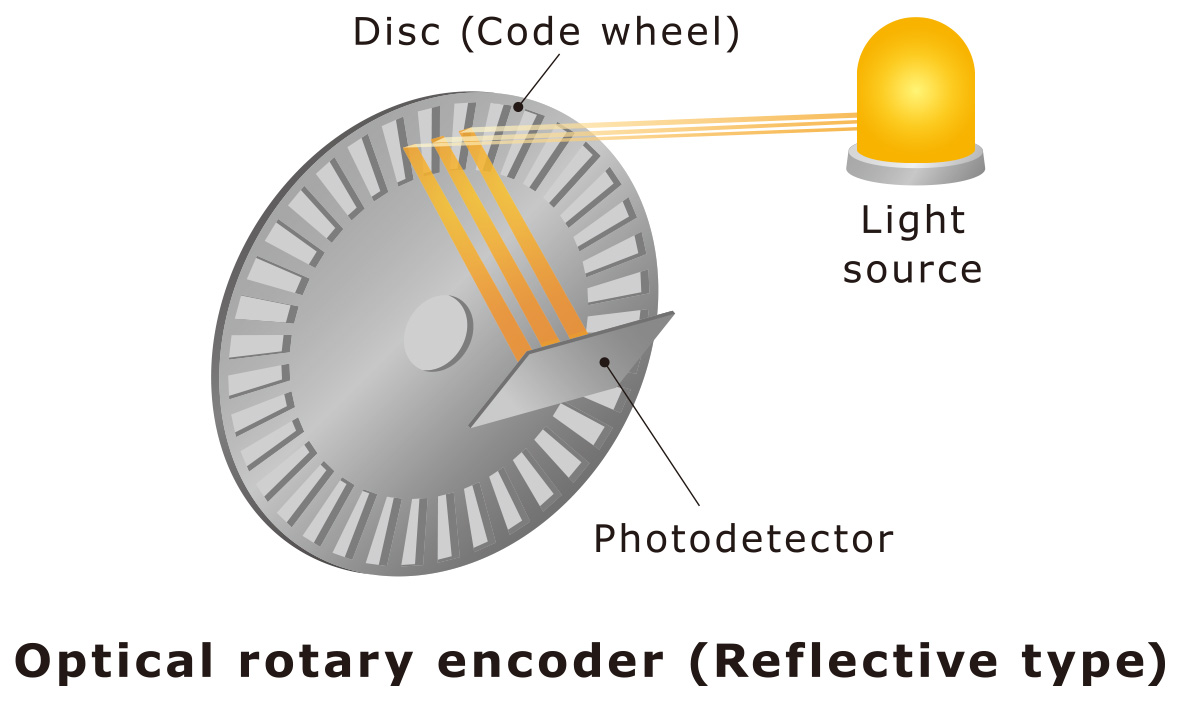
This type of encoder is often used as a sensor in robotics. It reads a disk with evenly spaced graduations. A code wheel with a rounded linear scale, which is a component of a linear encoder, is used, and the technology used to manufacture both is similar.
They are used in a wide variety of applications, from inexpensive ones incorporated into printers to high-precision control and measurement applications.
2) Signal output method
Incremental type
The rotation angle is measured by converting the number of detected pulses. The rotation speed is obtained from the pulse interval or the number of pulses in a unit time.

Fig. Absolut Encoder Disk
In the incremental type, only the change in the rotation of the disk is known, and the number of degrees of change in the sensor output from the reference position is counted and held in a counter or memory.
Absolute type
This type of encoders output the absolute value of the rotation angle, and the mechanical position is acquired immediately after power-on.

Fig. Incremental Encoder Disk
While the incremental type outputs only incremental values and requires origin alignment, the absolute type outputs a one-to-one correspondence between the disk angle of the scale pattern and the output code, so the absolute angle can always be known regardless of its power state.
Thus, the absolute type has the advantage of eliminating the need for origin alignment, but the scale pattern is more complex and the resolution tends to be lower than that of the incremental type.
| Feature\Type | Absolute | Incremental |
|---|---|---|
| High resolution | ✓ | |
| No homing required | ✓ | |
| Large feed rate | ✓ | |
| Noise immunity | ✓ | |
| Low price | ✓ |
3) Optical path
Optical encoders can be classified into “transmission type” and “reflection type” according to the optical path taken by the light-receiving element inside to detect the light.
Transmissive type
The transmission type refers to a method in which a light source and a light-receiving element are placed face to face through a space, and light is intercepted or transmitted between them.
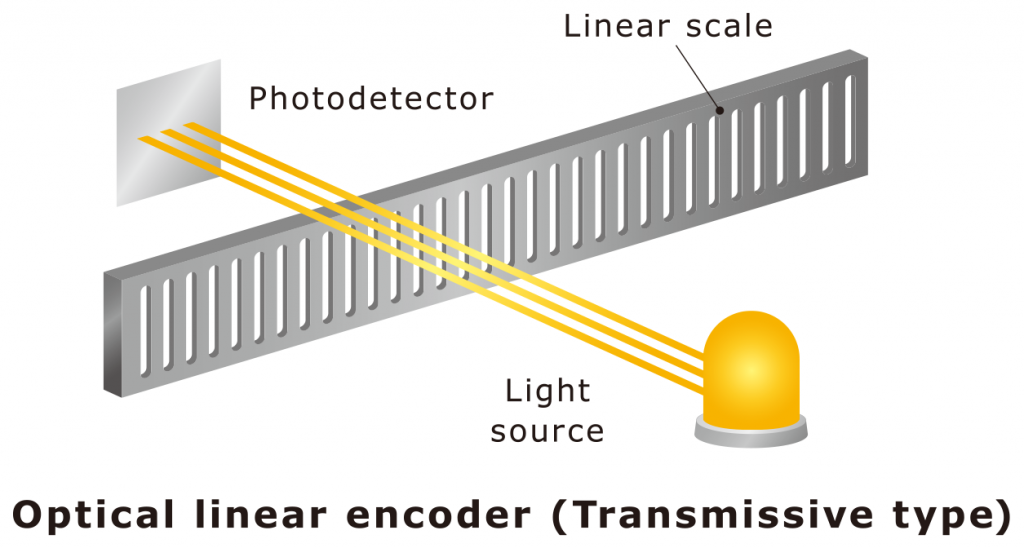
The advantages of the transmissive encoder are as follows.
- Easy to improve signal accuracy than the reflective encoder
- Easy to improve contamination resistance
- Relatively easy to design
On the other hand, it also has the following weaknesses:
- Narrow physical movement allowance
- Limited design flexibility
Reflective type
On the other hand, “Reflective type” refers to a method in which the light source and the light-receiving element are placed on the same plane, and a component that switches the reflection/non-reflection of light is placed above the light source and the light-receiving element.

The advantages of the reflective encoder are:
- Easy to be manufactured thinner and smaller
- Simple assembly process
However, it has the following weaknesses
- Low contamination resistance
- Low signal accuracy
| Feature\Type | Transmissive | Reflective |
|---|---|---|
| High signal accuracy | ✓ | |
| Contamination resistance | ✓ | |
| Simple structure | ✓ | |
| Miniaturization | ✓ | |
| Assembly time | ✓ |
Here are our products
Optical Encoder Wheels
Optical Encoder Structure
Optical encoder mainly consists of the following three parts.
Light Source
Most optical encoders use infrared light-emitting diodes as their light source. Laser diodes may also be used in high-resolution products.
Photodetectors
A photodiode or similar device is generally used as a light-receiving element. The light-receiving element is a diode, which transmits the input signal/current to the output side through light.
Encoder Scale
Encoder scales are components incorporated in encoders that switch the transmission/blocking or reflection/non-reflection of light (e.g., LEDs). The scale is engraved with slits (scales) at regular intervals, and light passing through or blocking the slits is called a transmission type, while light reflecting or non-reflecting is called a reflection type.
Encoder scales are indispensable components for motion control technology and are used in many fields, including industrial robots, positioning servos, production plant automation, and the automotive industry.
Here are our products
Optical Encoder Wheels
Where are Optical Encoders used?
Joints of Robot Arm

There are many types of mechanical position/posture sensors, but generally, manufacturers in robotics industry use articulated arms with rotary encoders placed at the joints.
It is necessary to use either a 3-DOF type that measures only position or a 6-DOF type that measures both position and posture depending on the number of joints to be measured.
In some special case, there is also a motion capture device with encoders placed at the positions corresponding to the joints of the human body to measure its movement.
Doors of Elevator

There is a motor controlling opening and closing the elevator door, and it requires low noise due to the close proximity of passenger.
There is an encoder used in the motor which controls the speed of the door movement. It also helps to determine the position of the doors.
Printers

Encoders are used to control the operation of ink heads of inkjet printers.
The encoder sends pulse signals to the industrial inkjet printer as the attached pulley rotates. The inkjet printer uses the interval between the pulse signals to recognize the speed of the object.
The use of an encoder in the printer makes it possible to print beautifully an accurately. Encoders are also used to control the rotating drum that moves the paper.
Machine tools

Encoders are used to control the horizontal movement of the table where the workpiece is placed.
For example, NC milling machines and electrical discharge machines require finishing accuracy in the range of a few microns to a few tens of microns. To achieve this, they require encoders with a resolution about 10 times higher than the required finishing accuracy.
Here are our products
Optical Encoder Wheels
How does an Optical Encoder work?
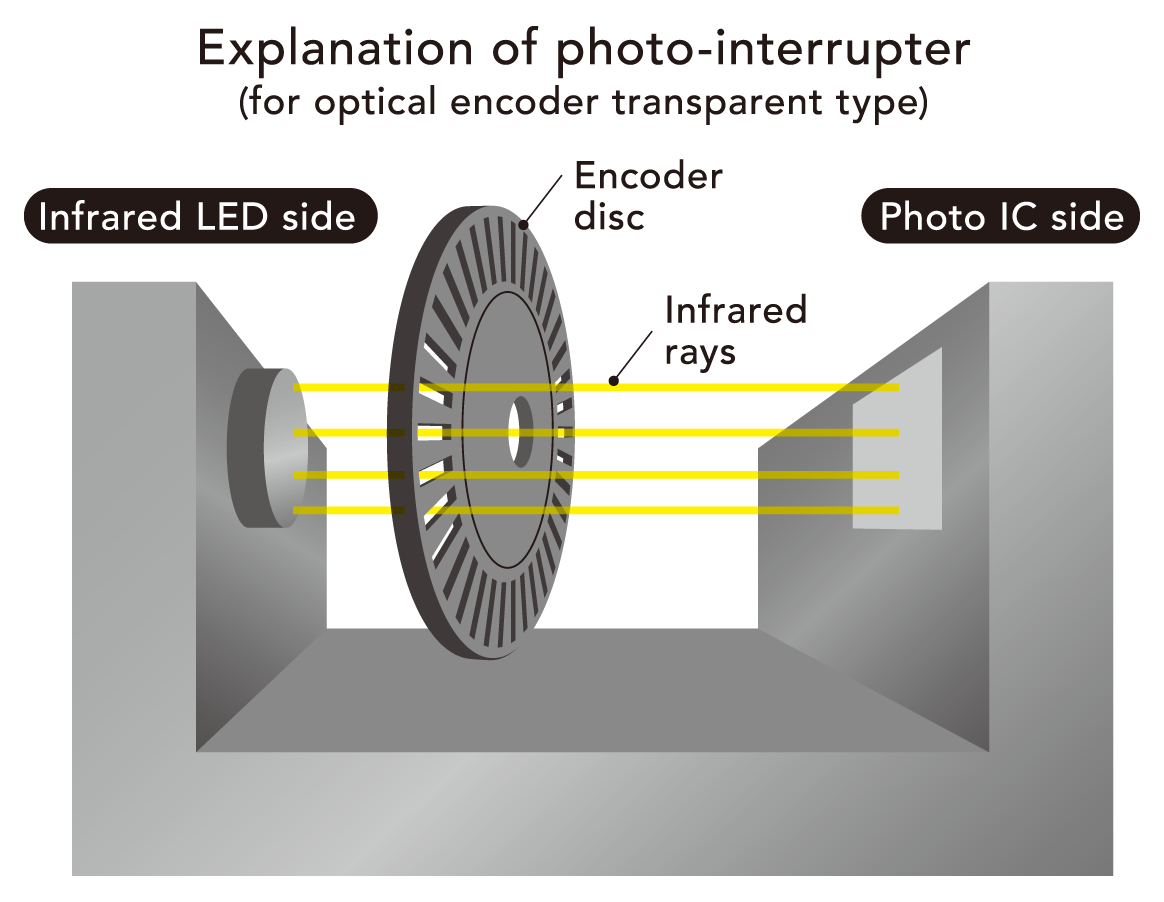
In this section, we will explain the principle of optical encoder operation using an optical transmissive rotary encoder as an example.
This type of encoder mainly consists of
- Light source (on the Infrared LED side)
- Photodetector (on the Photo IC side)
- Encoder disc engraved with bars that serve as scales
The optical encoder disk, which is used to measure the number of rotations of the motor, is mounted between the U-shaped parts shown in the illustration. This U-shaped part is called a “photo interrupter”.
The photo interrupter contains an infrared LED and a photo IC placed between the discs. When infrared light is irradiated, this mechanical part measures the number of times the LED light passes through the bar hole of the disc.
The number is converted into an angle to detect the rotation angle and speed of the disc.
How to choose an Optical Encoder
i) Model (Rotary or Linear?)
The first step in selecting an encoder is to decide whether to use a rotary or a linear encoder.
You can select an encoder based on whether the final motion of the drive system will be linear or rotary.
ii) Output method (incremental or absolute?)
Absolute type does not require homing because it provides absolute position information even if the power is turned off, while incremental type requires it, and may require various sensors for homing, which may be costly.
On the other hand, the incremental type has a simple structure and is relatively inexpensive. The incremental type is also suitable for measuring speed and direction of motion, rather than absolute values.
iii) Resolution and specifications (Does it have the appropriate size and resolution?)
It is common to select a resolution that provides 1/2 to 1/4 of the overall mechanical system accuracy.
Dimensions should be determined according to the system in which the encoder will be incorporated. This means that the size of the housing diameter, length, output shaft diameter (solid shaft or hollow shaft), etc. must be selected.
If you cannot find an off-the-shelf encoder with the appropriate resolution and size, consider a custom-made encoder.
Our specialty
We produce Optical Encoder Disks and Optical Linear Encoder Strips, which are essential for motion controlling technology and are currently used in many applications as follows.
- Industrial robotics
- Positioning servos
- Factory automation
- Auto industry
The “Optical Encoder Disk” is a disc-shaped scale built into a rotary encoder device .
The “Optical Linear Encoder Strip“ is a linearly shaped scale that is incorporated into an encoder device detecting the position of a linear axis and outputs it as position information.
Here are our products